Abstract
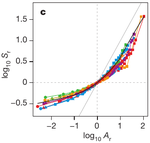
Despite the broad conceptual and applied relevance of how the number of species or endemics changes with area (the species–area and endemics–area relationships (SAR and EAR)), our understanding of universality and pervasiveness of these patterns across taxa and regions has remained limited. The SAR has traditionally been approximated by a power law, but recent theories predict a triphasic SAR in logarithmic space, characterized by steeper increases in species richness at both small and large spatial scales.
Here we uncover such universally upward accelerating SARs for amphibians, birds and mammals across the world’s major landmasses. Although apparently taxon-specific and continent-specific, all curves collapse into one universal function after the area is rescaled by using the mean range sizes of taxa within continents. In addition, all EARs approximately follow a power law with a slope close to 1, indicating that for most spatial scales there is roughly proportional species extinction with area loss. These patterns can be predicted by a simulation model based on the random placement of contiguous ranges within a domain.
The universality of SARs and EARs after rescaling implies that both total and endemic species richness within an area, and also their rate of change with area, can be estimated by using only the knowledge of mean geographic range size in the region and mean species richness at one spatial scale.